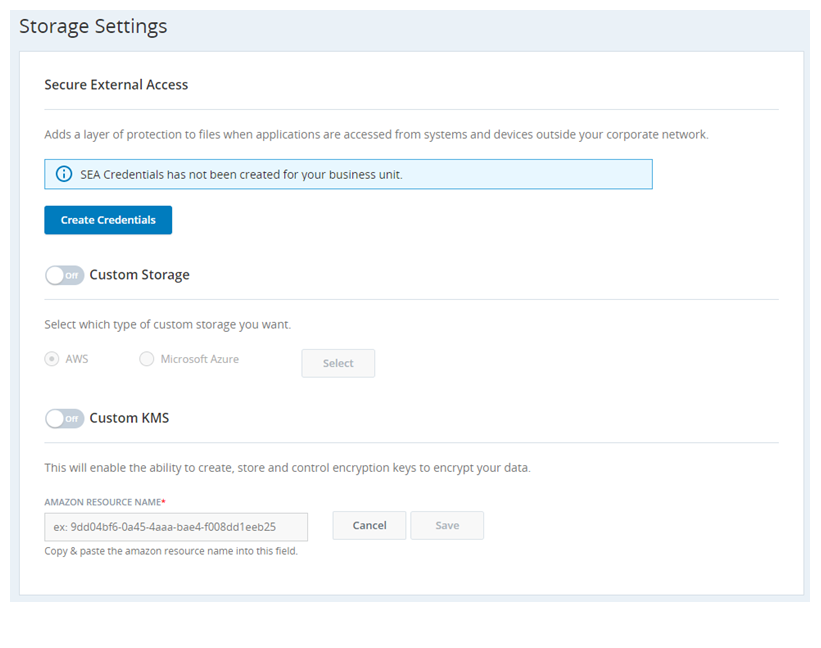
You can specify your own custom location for cloud storage, for files such as call recordings and screen recordings. Your primary option for custom storage is Amazon Web Services (AWS). If you are setting up custom storage for the first time, you also have Microsoft Azure as an additional option. To use Azure with CXone, your organization must already have Azure storage configured, including administrative keys and an existing bucket. If you turn off custom storage, your storage location reverts to the default system cloud storage.
Your custom AWS storage must be in the same AWS region as CXone.
Before configuring AWS (Amazon Web Services) storage, you need to create a custom S3 bucket with the required policies. For the SOP (standard operating procedure) document detailing how to create a custom S3 bucket, contact your CXone Account Representative.
Enable Custom Storage
Before you begin, ensure that custom storage is enabled for your
If you are on SanDisk with NICE CXone and you enable Cloud Storage and Custom Storage, then your files are moved from SanDisk storage to your custom AWS
- Click the app selector
 and select Admin.
and select Admin. - Click Cloud Storage > Storage Settings.
- Click the Custom Storage slider to On.
- Select AWS or Microsoft Azure.
- Configure the storage integration settings:
 For AWS:
For AWS:- Select the appropriate storage Region.
- Enter an existing storage Location name that is configured for the custom storage region that you selected.
 For Azure:
For Azure:You must acquire information for the following fields from Microsoft.
- Enter your Storage Account.
- Enter your Storage Container.
- Enter your Azure Access Key.
- Click Save and in the pop-up message, click Yes.
Ensure that you have the permissions required to save data on the storage location you specify. You should create only one custom storage location. If you are using both AWS storage and Custom KMS, ensure that the AWS region for both is the same.
When custom storage is enabled for your
Any files getting created after Custom Storage is set up are saved to Custom Storage right away. Files created before the Custom Storage is set up will not be transferred over to Custom Storage. Those files will continue to be in Cloud Storage Services. Such files can be accessed through the usual means, such as Contact History. The files left behind in Cloud Storage will continue to respect the Life Cycle Management rules that were set before Custom Storage was turned on.
Custom Storage Limitations
Custom storage includes multiple limitations. CXone Cloud Storage Services is the preferred storage method, as it provides rich functionality such as TTL, search, and efficient file management. Unless custom storage is required for your compliance requirements, contact your CXone Account Representative for CXone cloud storage.
General Limitations
- Files in Custom Storage are not named with your contact ID (unlike in SEA). The file name is an encrypted code and therefore cannot be matched with specific contact IDs.
- CXone does not support TTL rules for files in Custom Storage.
- Files that are stored in CXone's Cloud Storage before Custom Storage is enabled cannot be moved to Custom Storage.
- Once you move your files to Custom Storage, the files cannot return to CXone's Cloud Storage Services.
-
Files stored in Active Storage or Long-term Storage cannot be moved to a Custom Storage bucket.
AWS-specific Limitations
- Availability and operation of your custom S3 bucket is your own responsibility. It is recommended that you do not modify the IAM bucket-level policy. Changes in the IAM policy may result in CXone losing access to your S3 bucket.
- When the files are stored in your S3 bucket, they are encrypted. Hence, you cannot access the files directly and play them in your environment. You need to make use of CXone to playback any files.
Azure-specific Limitations
- Custom KMS is not supported.
- You must manage all administration with Microsoft, such as access keys, as your organization owns the Microsoft account.
- Only available if you do not already use AWS custom storage.
- You must handle data encryption and security of files at-rest.
- In case of failures when sending files to Azure, files will be stored on the default storage as backup. In this case, backed up files may be stored in a different region.